During the use of SY series syringe pumps (e.g., SY-01B, SY-03B, SY-08, etc.), users may encounter a specific phenomenon: the syringe pump can reset to the zero point normally when unloaded, but fails to complete the reset after being connected to a fluid system or when the outlet tubing is lengthened.
This issue prevents the device from finding the accurate initial position, thereby affecting the accuracy and reliability of all subsequent operations such as aspiration and dispensing. It is a critical failure point in automated systems.
To understand and resolve this issue, it is first necessary to understand the reset mechanism of the syringe pump:
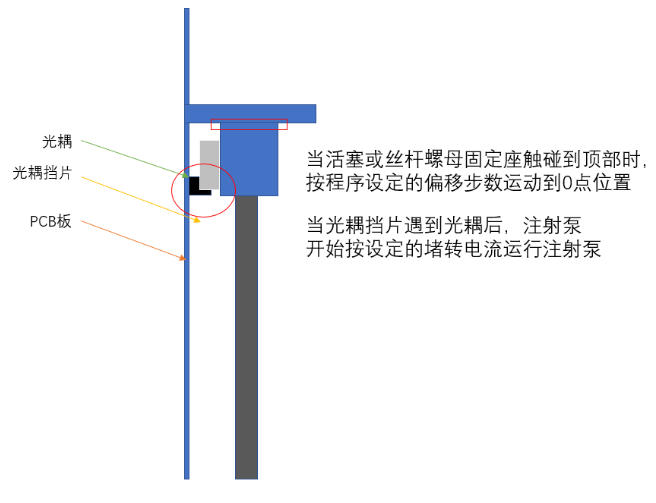
1. Reset Process: After the syringe pump starts, the piston moves upward (towards the syringe top). When the "photoelectric coupler shutter" on the piston triggers the limit photoelectric sensor, the motor will continue to run with a small, preset "Reset Stall Current" until the piston reaches the syringe top and stalls (i.e., can no longer advance). This position is marked as the mechanical top.
2. Zero Point Position: Subsequently, the piston retracts a fixed number of "offset steps" downward from the mechanical top. The position where it finally stops is the operational "zero point".
3. Root Cause: When connected to a system or when the tubing is lengthened, the fluid resistance (back pressure) increases significantly. The torque generated by the originally set reset stall current is insufficient to overcome this resistance and push the piston. This causes the piston to stop prematurely due to current limitation before reaching the true mechanical top, and the system mistakenly considers the reset successful. The "offset steps" retraction then starts from an incorrect starting point, leading to an inaccurate final zero point position.
To address the above phenomenon, the solution is divided into two methods depending on the communication protocol used by the syringe pump:
SY series syringe pump (e.g., SY-01B, SY-03B, SY-08, SY-09.SY-09S).
Serial communication cable (RS232/RS485)
Serial port debugging software-SerialComm
System with corresponding fluid tubing (to reproduce
Solution Steps
Case 1: Using ASCII Protocol
1. Connect Device: Correctly connect the syringe pump via the serial debugging software.
2. Send Command: The default starting value for the reset stall current is 5. You need to increment the current value by 1 step based on this value.
3. Test and Confirm: After each command to increase the current, attempt to execute the reset operation and observe if it can successfully reset to the zero point. Repeat this process until the syringe pump can reset stably under load.
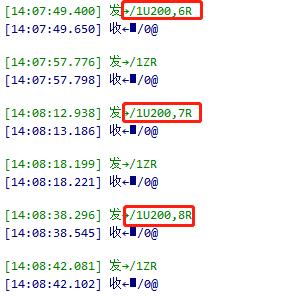
Example Command Flow
1. Set current to 6 and reset → Observe result
2. If fails, set current to 7 and reset → Observe result
3. ... Increment sequentially until successful.
Case 2: Using Custom Protocol
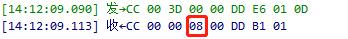
1. Query Current Value: First, use command 0x3D to query the current reset stall current parameter value of the syringe pump.
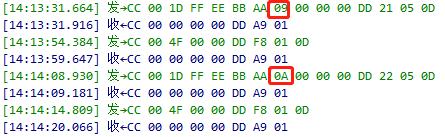
2. Increase and Test: Based on the queried current value, gradually increase the reset stall current value in increments of 1.
3. Iterate and Verify:Each time a new value is set, command the syringe pump to perform a reset and test whether it can successfully reset to zero under load. Continue this process until the problem is resolved.
Note: Please refer to the device communication protocol manual for specific command formats.
1. Root Cause: When a normally functioning syringe pump fails to reset due to changes in its operating environment (e.g., connected to a system, tubing lengthened), the root cause is increased system resistance, while the default reset driving force (stall current) is insufficient.
2. General Solution: Increasing the reset stall current is a direct and effective method to solve this type of problem. By gradually increasing the current, sufficient torque is provided for the syringe pump to overcome the system back pressure, ensuring it can accurately reset to the mechanical zero point.
3. Final Measure: If the problem persists after adjusting the stall current to a very high value, potential hardware issues such as mechanical jamming, motor failure, or drive circuit abnormalities should be considered. In this case, contact technical support promptly for further investigation.
By following the systematic steps in this guide, you can quickly diagnose and resolve syringe pump reset failures caused by changes in environmental load, ensuring the stable operation of your fluid control system.